Terminal Blocks: The Building Blocks of Industrial Control Cabinets
By Misumi
Motion Control Machine Building noadsLB
Sponsored by Misumi
Picking the right terminal block depends on wire gauge, system voltage, current requirements, pole count and cabinet environment.
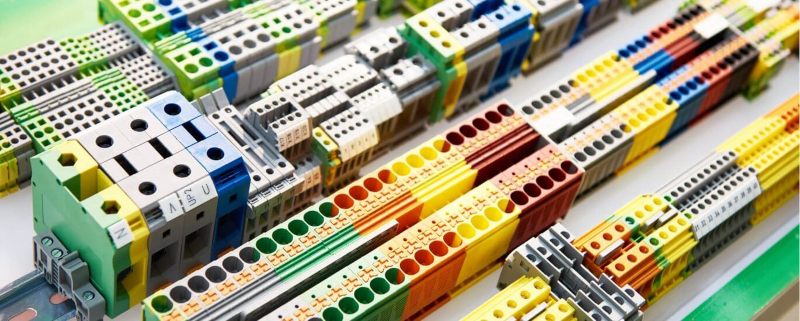
A terminal block is a modular housing with an insulated body that secures two or more wires together. The insulating body of a terminal block consists of a current-carrying element, a clamping element, and a mounting arrangement. Terminal blocks are used wherever electrical systems need to stay safely connected, organized, and secure. They provide a semi-permanent wire connection that can easily be removed, modified, and replaced for inspection or repair.
Selecting The Appropriate Terminal Block
Since terminal blocks are important for the electrical performance and prevention of safety hazards, when choosing the most suitable terminal block one must consider the wire gauge, overall system voltage, current requirements, pole count, and cabinet environment.
- Wire Gauge (Wire Size) – The minimum and maximum wire size (AWG/mm2) will be a function of the voltage/ current rating. Stranded or multi-core wire is used for screw terminals and single-core is typically used for push-in-style terminal blocks.
- Voltage Rating – The maximum system voltage of the application must be less than the voltage rating.
- Current Requirements – It is best practice to use terminal blocks that are rated at least 150% of the maximum current in the system.
- Pole Count – The number of individual circuits within the terminal block is also known as pole count. This can range from 1 to 24 poles.
- Control Cabinet Environment – Depending on the chosen size of the control cabinet, configuration, and the number of additional components, working space can be an issue. Therefore, terminal blocks have varied wiring entry options. These include horizontal, vertical, and 45-degree angled.
Terminal Blocks typically have several different wire connection technologies that secure the wire to the terminal.
These include:
- Screw Terminal
- Push Button
- Push-in
- Barrier (European Connectors)
- IDC (insulation displacement connector)
- Spring Loaded
Types of Terminal Blocks
Feed-thru Terminal Blocks – Are used to connect 2 wires together for a wire-to-wire connection. This type has one input and one output contact. Variations of these include single, dual, and multi-level modules.
 Ground Terminal Blocks – These blocks look like single-level feed terminals, however, the metal connection where the wire is terminated is grounded to the electrical panel or DIN rail.
Ground Terminal Blocks – These blocks look like single-level feed terminals, however, the metal connection where the wire is terminated is grounded to the electrical panel or DIN rail.
 Fused Connection Terminal Blocks – The metal connection strip is replaced with a fuse. This product can also include an LED to alert you of a malfunction. This is ideal for PLC applications providing protection against over current and short circuit conditions.
Fused Connection Terminal Blocks – The metal connection strip is replaced with a fuse. This product can also include an LED to alert you of a malfunction. This is ideal for PLC applications providing protection against over current and short circuit conditions.
Multi-Level Terminal Blocks – Allow for several terminations in one block. One can create levels or tiers of termination points to provide space-saving, greater functionality, and future system expansion. Ideal for use with actuators and sensors due to the number of wires they require.
 Disconnect Terminal Blocks – AKA switch blocks. Allows wires to be easily disconnected just by lifting a lever or switch. Meaning it is not necessary to remove wires.
Disconnect Terminal Blocks – AKA switch blocks. Allows wires to be easily disconnected just by lifting a lever or switch. Meaning it is not necessary to remove wires.
 I/O Blocks and Sensor Blocks – I/O blocks are used to make a connection between a device and a controller. Whereas sensor blocks handle 3 or 4 wire devices such as proximity sensors.
I/O Blocks and Sensor Blocks – I/O blocks are used to make a connection between a device and a controller. Whereas sensor blocks handle 3 or 4 wire devices such as proximity sensors.
Power Distribution Blocks – It is a convenient, economical, and space-saving way to distribute power from a single input source to multiple outputs. With a large number of wires these terminal blocks provide a well-organized control panel.
Many control panels can often appear disorganized and complex making it difficult to troubleshoot and maintain. Exposed or unsecured electrical wires are unsafe for the system and user. Terminal blocks provide an organized, clean, and professional-looking control panel. Additionally, using different housing colors and/or marking tags on each terminal block will aid in the identification of a specific circuit.
While each specific block type may be used in a different context, all terminal blocks provide the same function of connecting electrical components in a safe and reliable manner for complex electrical system connections.
MISUMI offers a wide range of terminal blocks and ancillary products from all the top manufacturers to meet your wire-to-board design challenges. Check out the selection here.