Made In Space awarded NASA contract for flight demo of AM system
By DE Staff
General AerospaceFirm’s Robotic Manufacturing and Assembly System, Archinaut, to 3D print 10-meter solar arrays in orbit.
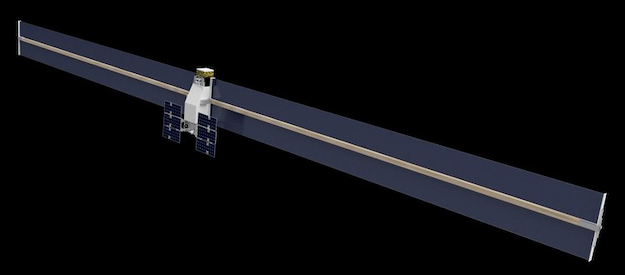
The Archinaut One satellite will use robotic manufacturing and assembly to manufacture two 10-meter solar arrays on orbit. (Photo credit: Made In Space)
“Autonomous, robotic manufacturing and assembly will reshape the landscape of space exploration and space infrastructure and we are taking a monumental step towards that future.” said Andrew Rush, MIS president and CEO. “Through our partnership with NASA, we will build a space-optimized asset on-orbit, for the first time, that will prove the efficacy of this technology, reduce the risk posture, and manifest new opportunities for in space manufacturing.”
This flight demonstration contract award follows a successful ground-based testing campaign of Archinaut’s core additive manufacturing and robotic technologies, qualifying the Archinaut platform for spaceflight.
The objective of Archinaut’s flight demonstration mission, dubbed Archinaut One, is to construct two 10-meter solar arrays, on orbit, to power an ESPA-class satellite. Once on orbit, Archinaut One will employ its extended structure additive manufacturing capabilities and advanced robotics to manufacture and assemble the satellite’s power system. The Archinaut-created solar arrays will yield nearly 5x the power currently available to ESPA-class satellites.
“The Archinaut One mission is a critical proof point to validate the use of robotic manufacturing and assembly for space exploration and commercialization activities” said Michael Snyder MIS Chief Engineer. “These technologies allow us to circumvent the design constraints imposed by the launch environment and create space optimized structures and assemblies thereby demonstrating unprecedented capabilities.”
In support of Archinaut’s flight demo mission, MIS will continue its partnership with Northrop Grumman while involving other companies and universities to successfully demonstrate this transformational technology. Northrop Grumman supported Archinaut development during phase I of the program.
The Archinaut One mission will demonstrate transformative, near-term benefits for the satellite industry. Robust small satellite power systems, manufactured on-orbit, would reduce launch mass and cost while increasing capabilities as small satellites could host power-intensive payloads previously reserved for larger platforms. These benefits could drastically lower the barrier of entry for new users and revolutionize satellite design.
www.madeinspace.us